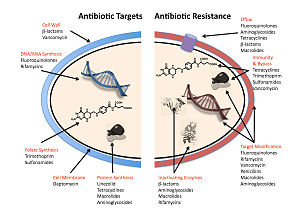
ANTIBIOTICS RESISTANCE

Antimicrobial resistance happens when microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites) change when they are exposed to antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics). Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
As a result, the medicines become ineffective and infections persist in the body, increasing the risk of spread to others.
Why is antimicrobial resistance a global concern?
New resistance mechanisms are emerging and spreading globally, threatening our ability to treat common infectious diseases, resulting in prolonged illness, disability, and death.
Without effective antimicrobials for prevention and treatment of infections, medical procedures such as organ transplantation, cancer chemotherapy, diabetes management and major surgery (for example, caesarean sections or hip replacements) become very high risk.
Antimicrobial resistance increases the cost of health care with lengthier stays in hospitals and more intensive care required.
Antimicrobial resistance is putting the gains of the Millennium Development Goals at risk and endangers achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
What accelerates the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance?
Antimicrobial resistance occurs naturally over time, usually through genetic changes. However, the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials is accelerating this process. In many places, antibiotics are overused and misused in people and animals, and often given without professional oversight. Examples of misuse include when they are taken by people with viral infections like colds and flu, and when they are given as growth promoters in animals and fish.
Antimicrobial resistant-microbes are found in people, animals, food, and the environment (in water, soil and air). They can spread between people and animals, and from person to person. Poor infection control, inadequate sanitary conditions and inappropriate food-handling encourage the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
Present situation
Resistance in bacteria
Antibiotic resistance is present in every country.
Patients with infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria are at increased risk of worse clinical outcomes and death, and consume more health-care resources than patients infected with non-resistant strains of the same bacteria.
Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae – common intestinal bacteria that can cause life-threatening infections – to a last resort treatment (carbapenem antibiotics) has spread to all regions of the world. K. pneumoniae is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections such as pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and infections in newborns and intensive-care unit patients. In some countries, because of resistance, carbapenem antibiotics do not work in more than half of people treated for K. pneumoniae infections.
Resistance in E. coli to one of the most widely used medicines for the treatment of urinary tract infections (fluoroquinolone antibiotics) is very widespread. There are countries in many parts of the world where this treatment is now ineffective in more than half of patients.
Treatment failure to the last resort of medicine for gonorrhoea (third generation cephalosporin antibiotics) has been confirmed in at least 10 countries (Australia, Austria, Canada, France, Japan, Norway, Slovenia, South Africa, Sweden and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland).
WHO recently updated the treatment guidelines for gonorrhoea to address emerging resistance. The new WHO guidelines do not recommend quinolones (a class of antibiotic) for the treatment of gonorrhoea due to widespread high levels of resistance. In addition, treatment guidelines for chlamydial infections and syphilis were also updated.
Resistance to first-line drugs to treat infections caused by Staphlylococcus aureus—a common cause of severe infections in health facilities and the community—is widespread. People with MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) are estimated to be 64% more likely to die than people with a non-resistant form of the infection.
Colistin is the last resort treatment for life-threatening infections caused by Enterobacteriaceae which are resistant to carbapenems. Resistance to colistin has recently been detected in several countries and regions, making infections caused by such bacteria untreatable.
Resistance in tuberculosis (TB)
WHO estimates that, in 2014, there were about 480 000 new cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), a form of tuberculosis that is resistant to the 2 most powerful anti-TB drugs. Only about a quarter of these (123 000 cases) were detected and reported. MDR-TB requires treatment courses that are much longer and less effective than those for non-resistant TB. Globally, only half of MDR-TB patients were successfully treated in 2014.
Among new TB cases in 2014, an estimated 3.3% were multidrug-resistant. The proportion is higher among people previously treated for TB, at 20%.
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB), a form of tuberculosis that is resistant to at least 4 of the core anti-TB drugs, has been identified in 105 countries. An estimated 9.7% of people with MDR-TB have XDR-TB.
Resistance in malaria
As of July 2016, resistance to the first-line treatment for P. falciparum malaria (artemisinin-based combination therapies, also known as ACTs) has been confirmed in 5 countries of the Greater Mekong subregion (Cambodia, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Thailand and Viet Nam). In most places, patients with artemisinin-resistant infections recover fully after treatment, provided that they are treated with an ACT containing an effective partner drug. However, along the Cambodia-Thailand border, P. falciparum has become resistant to almost all available antimalarial medicines, making treatment more challenging and requiring close monitoring. There is a real risk that multidrug resistance will soon emerge in other parts of the subregion as well.The spread of resistant strains to other parts of the world could pose a major public health challenge and jeopardize important recent gains in malaria control.
A “WHO Strategy for Malaria Elimination in the Greater Mekong subregion (2015-2030)” was endorsed by all 5 countries, as well as China.
Resistance in HIV
In 2010, an estimated 7% of people starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) in developing countries had drug-resistant HIV. In developed countries, the same figure was 10–20%. Some countries have recently reported levels at or above 15% amongst those starting HIV treatment, and up to 40% among people re-starting treatment. This requires urgent attention.
Increasing levels of resistance have important economic implications as second and third-line regimens are 3 times and 18 times more expensive, respectively, than first-line drugs.
Since September 2015, WHO has recommended that everyone living with HIV start on antiretroviral treatment . Greater use of ART is expected to further increase ART resistance in all regions of the world. To maximize the long-term effectiveness of first-line ART regimens, and to ensure that people are taking the most effective regimen, it is essential to continue monitoring resistance and to minimize its further emergence and spread. In consultation with countries, partners and stakeholders, WHO is currently developing a new “Global Action Plan for HIV Drug Resistance (2017-2021)“.
Resistance in influenza
Antiviral drugs are important for treatment of epidemic and pandemic influenza. So far, virtually all influenza A viruses circulating in humans were resistant to one category of antiviral drugs – M2 Inhibitors (amantadine and rimantadine). However, the frequency of resistance to the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir remains low (1-2%). Antiviral susceptibility is constantly monitored through the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System.
Need for coordinated action
Antimicrobial resistance is a complex problem that affects all of society and is driven by many interconnected factors. Single, isolated interventions have limited impact. Coordinated action is required to minimize the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance.
All countries need national action plans on AMR.
Greater innovation and investment are required in research and development of new antimicrobial medicines, vaccines, and diagnostic tools.
WHO’s response
WHO is providing technical assistance to help countries develop their national action plans, and strengthen their health and surveillance systems so that they can prevent and manage antimicrobial resistance. It is collaborating with partners to strengthen the evidence base and develop new responses to this global threat.
WHO is working closely with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) in a ‘One Health’ approach to promote best practices to avoid the emergence and spread of antibacterial resistance, including optimal use of antibiotics in both humans and animals.
A global action plan on antimicrobial resistance was adopted by Member States at the Sixty-eighth World Health Assembly and supported by the governing bodies of FAO and OIE in May and June 2015. The goal of the global action plan is to ensure, for as long as possible, continuity of successful treatment and prevention of infectious diseases with effective and safe medicines that are quality-assured, used in a responsible way, and accessible to all who need them.